Antibody hit expansion
Immune repertoires contain greater diversity than screening methods can interrogate. Moreover, any selection, panning, or filtering process often have biases or limitations that exclude valuable antibodies. High-throughput sequencing allows discovery teams to expand hits to millions of clones and extend the limits of screening technologies. Among this larger pool of clones desirable properties like liability-free proteins or high thermostabilities can be selected for amongst the right affinity and function.

Mining NGS repertoires to pick better binders with optimal developability profiles
Traditionally, hybridoma discovery workflows rely on the expression of a limited number of antibody candidates for testing with laboratory assays. Single B cell screening protocols and technologies like the Beacon can interrogate hundreds to thousands of clones. These approaches provide a small selection of well-characterized antibodies but unavoidably miss many antibodies with potentially better properties in a immune or synthetic repertoire. Antibodies not captured in immunization with similar sequences to known binders might have higher affinity, better thermostability or solubility, or less developmental liabilities. Combining these well-characterized antibody sequences with larger bulk-NGS or paired-chain sequencing approaches (e.g., 10x Genomics) enables researchers to expand and diversify the candidate pool and find better antibodies missed upon selection.
This expansion into a larger repertoire is especially relevant in in-vivo immunization or disease approaches where the animal/subject’s immune system works to generate the best antibodies against a given target. The lineages generated can be used to understand the antibody evolution and select the best candidates generated. Furthermore, mutations in this evolutionary branches can be combined to obtain synergies in binding strength yielding antibodies with superior properties than those naturally generated.
Antibody discovery simplified
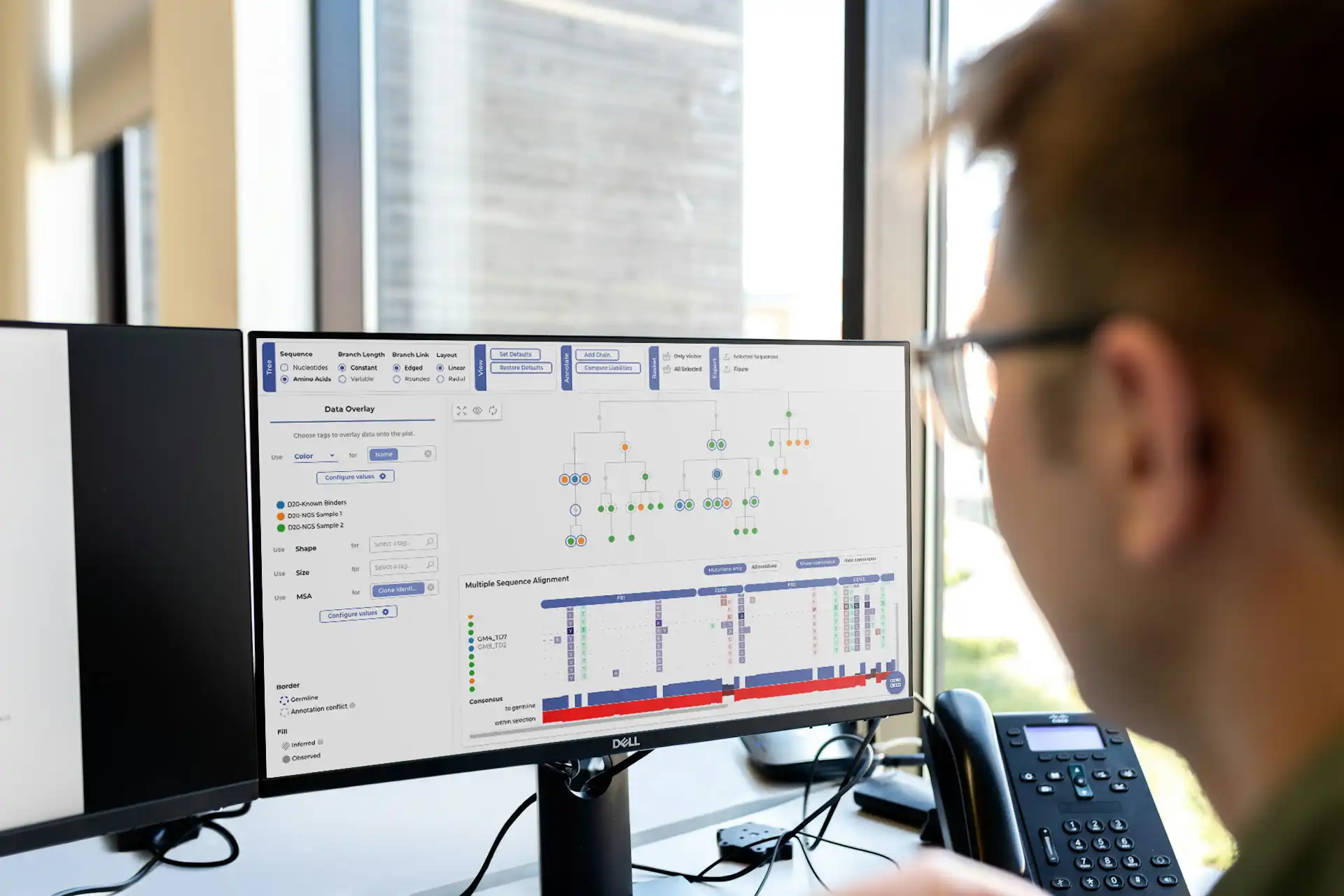
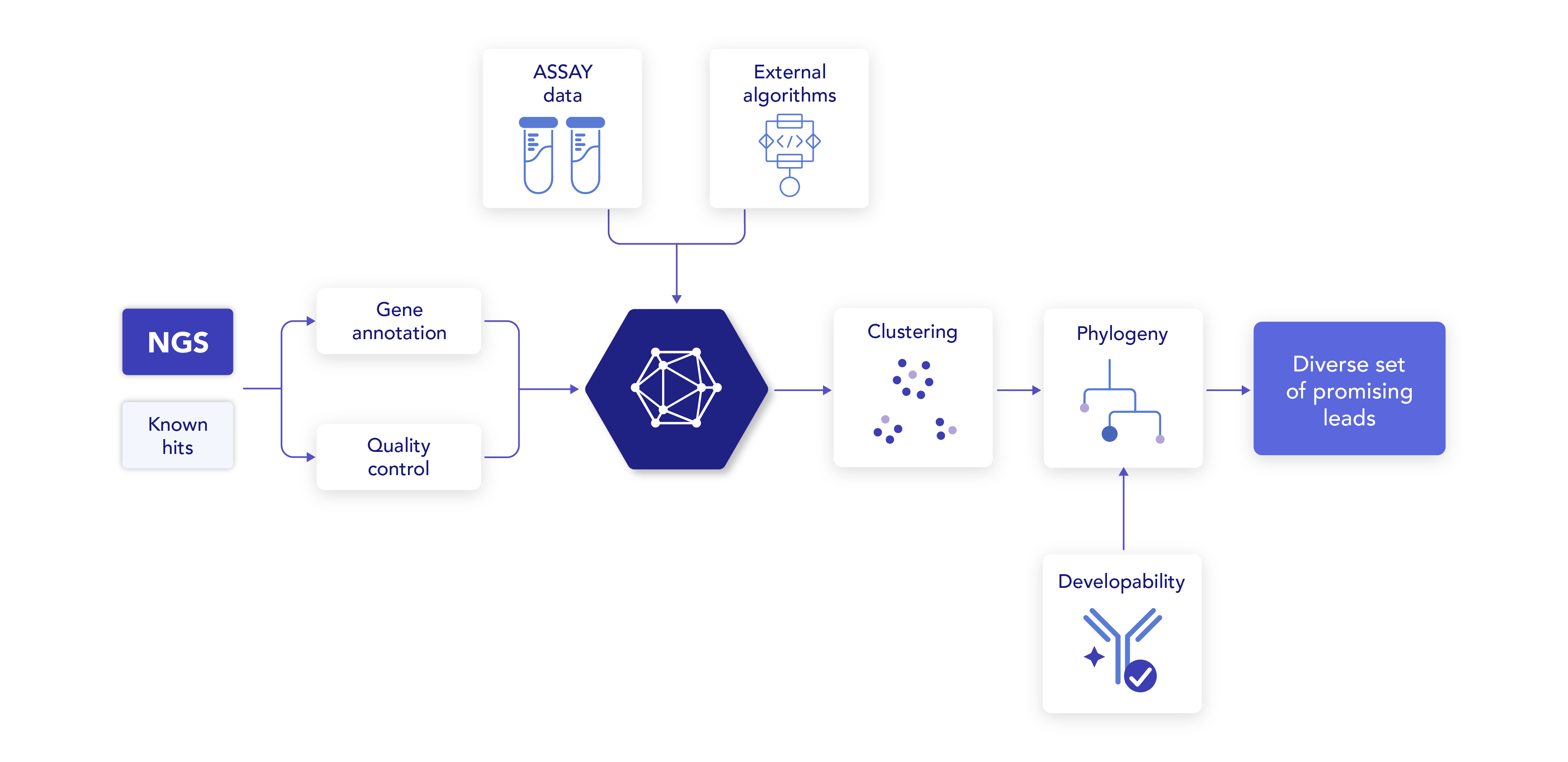
Accurate repertoire processing and annotation
Profile any NGS or paired chain data (using barcodes, linkers or clone/well identifiers) and annotate all relevant regions and affinity maturation (SHM).
A 360 view of your data
Import assay data (metadata) of characterized antibodies with their sequences.
Combining all datasets
Cluster bulk NGS or single-cell barcoded data with Sanger sequences of characterized antibodies based on sequence similarity and other immunologically relevant features.
Easily identify clusters of interest
Select clusters where known binders are present and prioritize them using the metadata linked to the characterized sequences.
Antibody developability assessment
Use high-throughput structural modeling to predict exposed liabilities and assess the developability of candidates with confidence and ease.
Maximum insights
Explore lineages of interest to identify antibody candidates with desired characteristics (e.g., higher affinity maturation or fewer liabilities) and interesting mutations).
How it works
- Flexible analysis configurations
- Interactive visualizations
- Sophisticated metadata integration
- Automated workflows
Learn more about the most powerful platform for BCR repertoire analysis
Easily integrate any assay data from wet lab experiments and compute structure-based developability profiles in silico to pick the optimal set of antibodies.
Discover how you can easily identify highly enriched candidates in your antibody display campaigns.
Trusted by industry leaders