Why ENPICOM
For nearly a decade, ENPICOM has been driving biologics discovery and development forward with robust bioinformatics solutions and services that integrate computational and biological expertise.
Faster AI learning cycles after full implementation
Faster data consolidation across instruments, vendors, and sites
Reduction in molecules experimentally tested
Next-generation biologics discovery starts with
unified data, tools, and teams
Biologics research generates complex, fragmented, and siloed datasets scattered across instruments, vendors, CROs, and global teams. Without structured, unified, and accessible data, even the best AI remains underutilized.
At ENPICOM, we developed a three-step approach that provides a clear path to successfully integrating AI into antibody discovery and development workflows.
ENPICOM’s blueprint to AI adoption
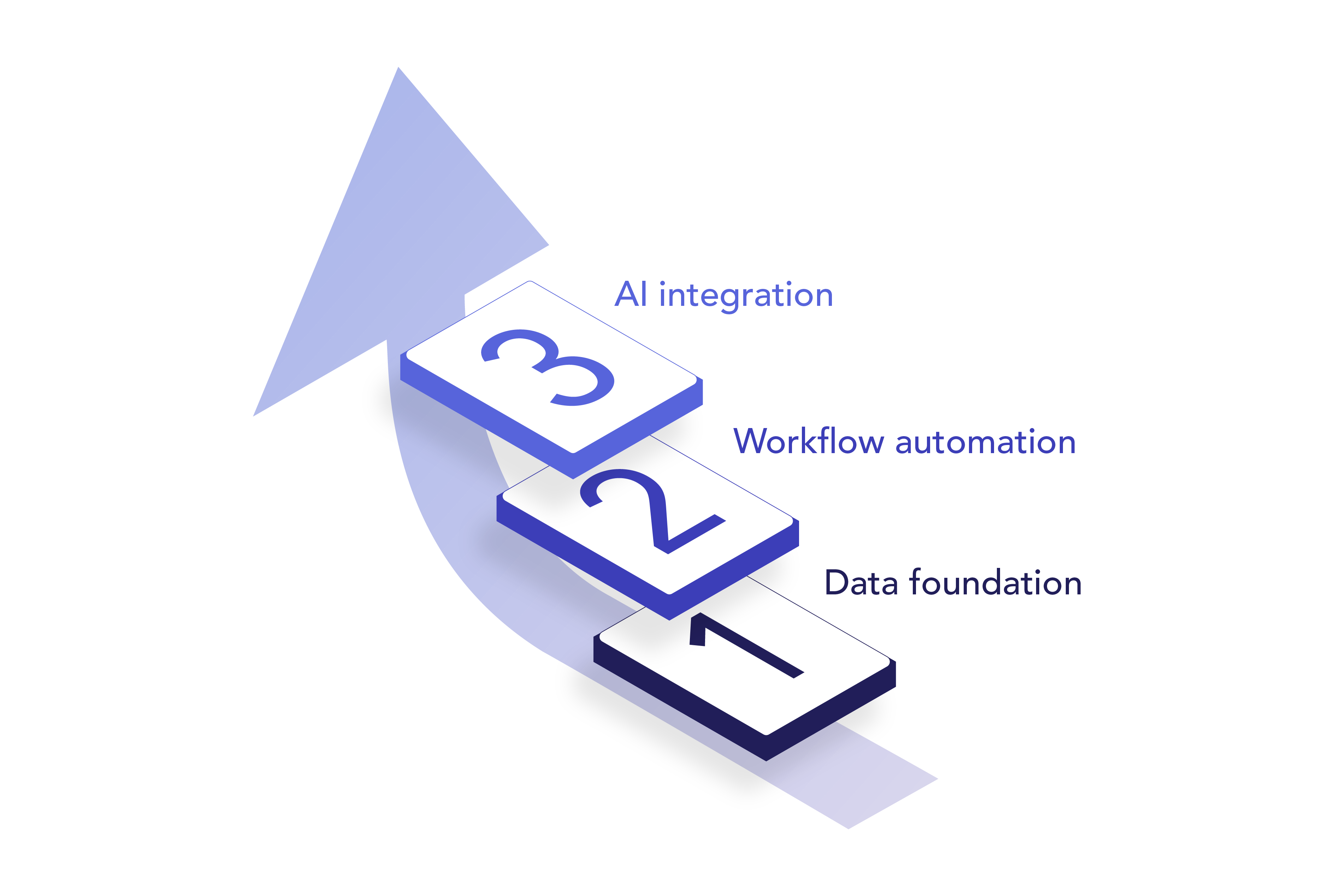
Data foundation
A structured, scalable, and integrated data architecture for well-labelled, accessible, and harmonized datasets for efficient AI model training and discovery.
Workflow automation
Standardized and automated bioinformatics workflows within a unified ecosystem, consolidating tools and data processing.
AI integration
A streamlined approach to train and track models, along with an automated system for deploying models and embedding them into intuitive data analysis workflows.
Unlocking the promise of scientific AI
ENPICOM combines high-performance data architecture, cross-domain expertise, and advanced tools to accelerate biologics discovery and development.
Years of experience in integrating biologics data for discovery and engineering
Professionals skilled in immunology, machine learning, and software engineering
Increase in the number of samples processed per minute
For executives
AI holds an immense potential for innovation and cost-savings, but it requires moving from single ML experiments to production-ready ML models and applying AI effectively at scale. Our platform integrates lab and AI efforts, enhancing data utilization and accelerating the development of new biologics.
For lab scientists
The volume of research data and potential for AI models are growing exponentially. No-code tools help lab scientists to easily perform advanced analyses without bioinformatics support. Nothing should stand between scientists and their data.
Simplify discovery workflow
Simplify discovery workflow
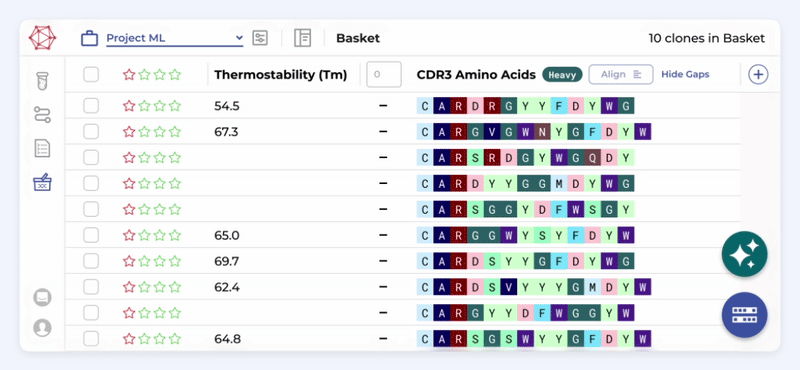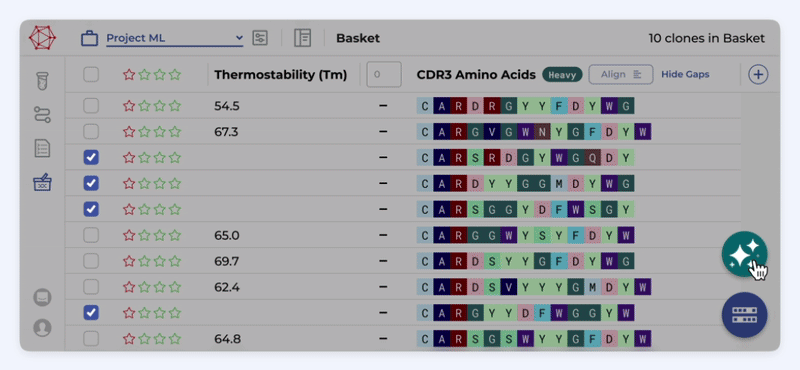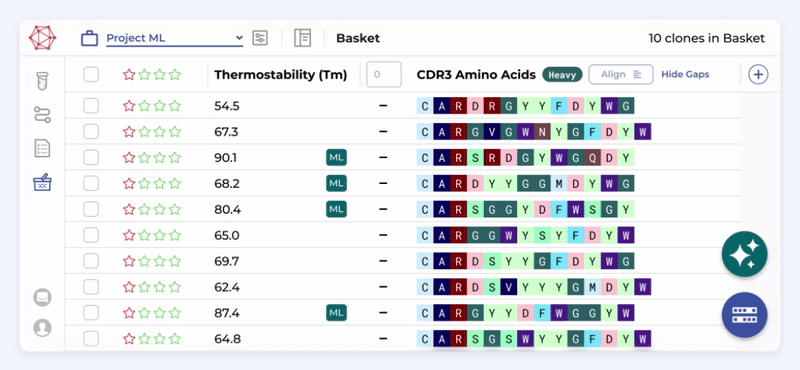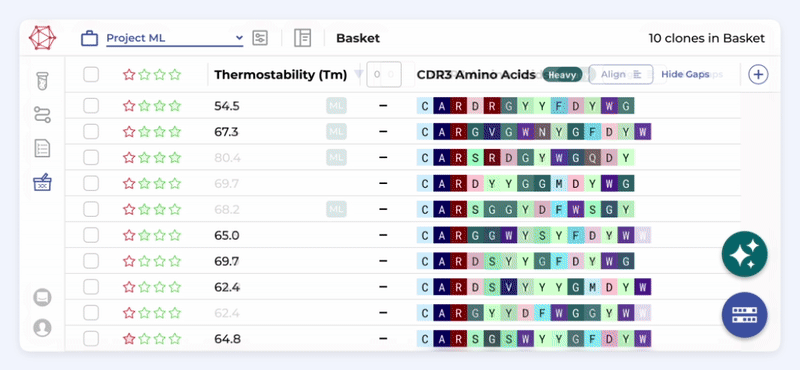
Define your workflow in a code-free environment, integrating and analyzing sequencing data and metadata effortlessly. Enhance efficiency and productivity without needing bioinformatics expertise or support.
Independently access ML models
Accelerate decision-making and improve your candidate selection and optimization process with seamless AI integration. Utilize ML models within the same environment where you select your candidates.
Select better candidates more efficiently
Use state-of-the-art tools designed for biologics discovery.
Unify data access
Navigate all your scientific data easily in a fully searchable and contextualized environment, breaking down data silos.
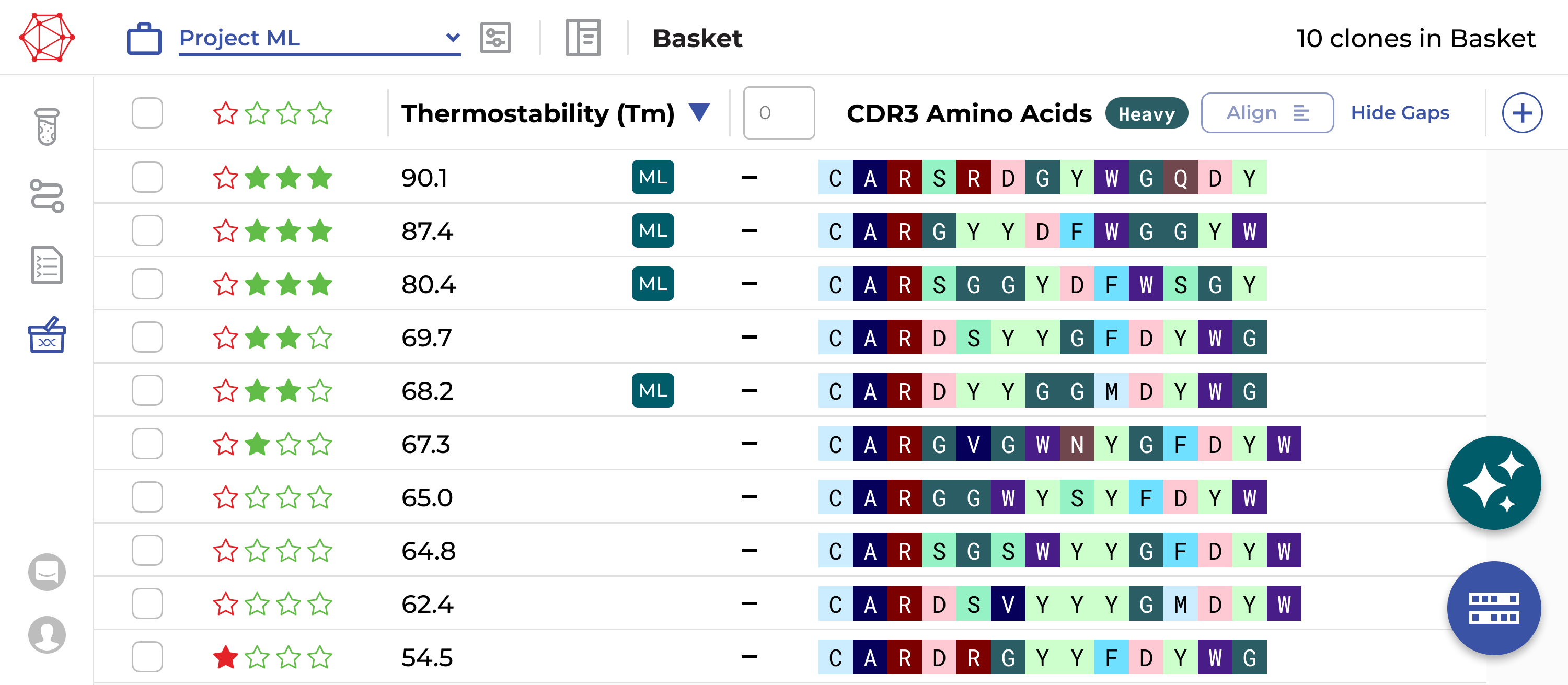
For ML scientists
ML model and experiment management, reproducibility and deployment consistency poses many challenges. By simplifying ML workflows, we enable data scientists to focus on developing and perfecting models, ensuring a seamless path from experimentation to production.
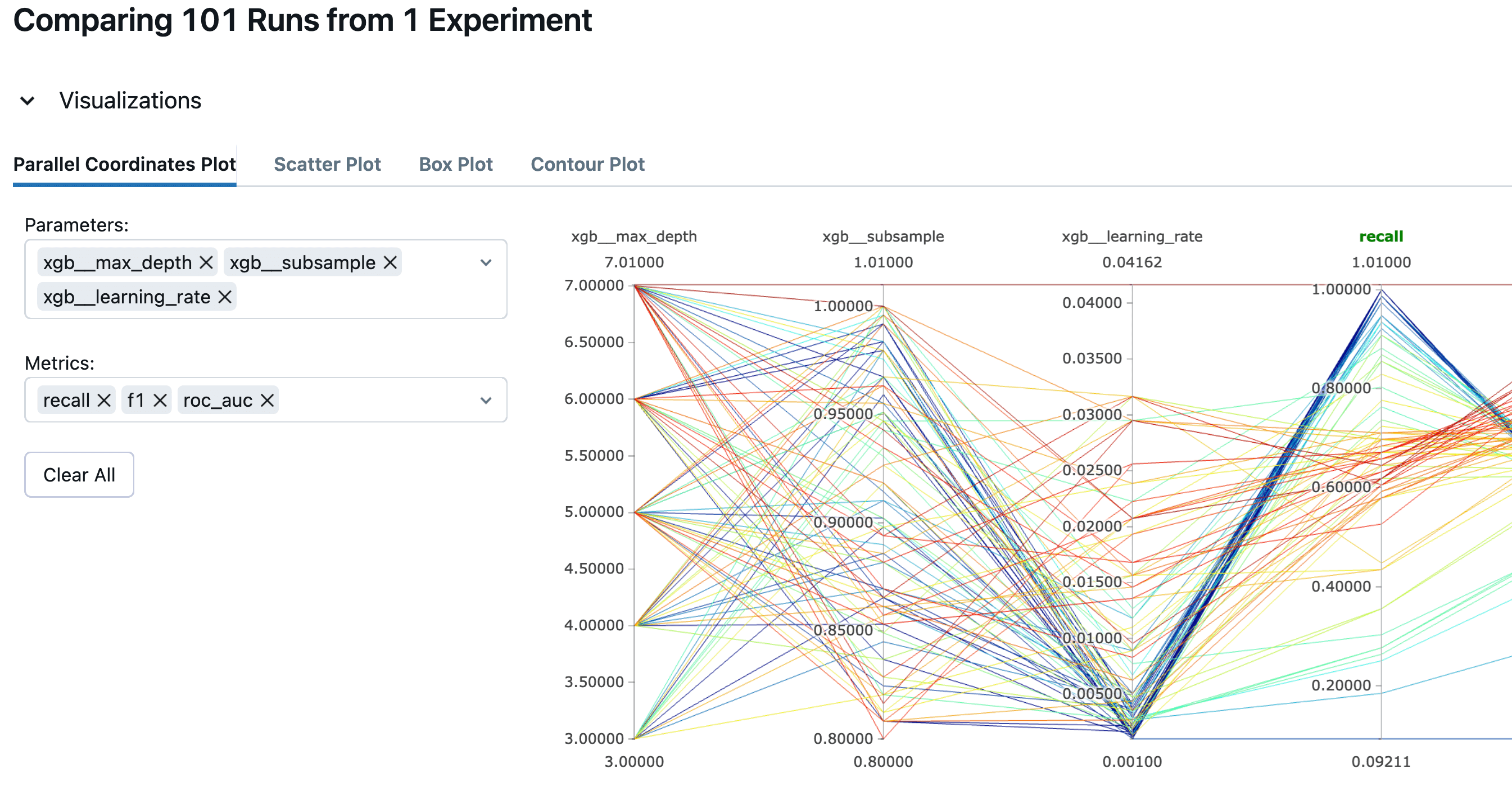
Efficient model management
Train, track and refine models, from experimentation to production, ensuring high-performance and efficient workflows.
Boost experimentation
Push ML experiments to production faster, running thousands of experiments iteratively and collaboratively to achieve breakthroughs quickly.
Future-ready ML systems
Overlooking scalability during internal development often leads to high maintenance costs, poor user experience, and huge inefficiencies. Utilize maintainable, modular systems designed to handle data for thousands of experiments, avoiding bottlenecks.
Bridge lab and data science
Access structured and scalable data repository where lab data is stored. Automate and scale ML workflows in one collaborative environment where lab and data science teams can utilize research findings and progress ensuring efficient collaboration.
Prevent biases in ML development
Implement consolidated analysis workflows to effectively detect and mitigate biases, enhancing the fairness and accuracy of your models.
Leaders in scientific research choose ENPICOM













Power your ML journey with seamless collaboration between data and lab scientists
Contact us for a personalized demo or consultation.